

Wa_english_title: "2nd Gen Intel® Xeon® Scalable Processors Datasheet, Vol. Wa_emt_org: "emtorganizationalstructure:dpgdataplatformsgroup", Wa_emtsubject: "emtsubject:itinformationtechnology/enterprisecomputing", Wa_rdcproducts: "rdcproducts:processors/intelxeonprocessorsnid46922/2ndgenerationintelxeonscalableprocessorsnid67653", Wa_upeproducts: "upeproducts:processors/intelxeonscalableprocessors/intelxeongoldprocessors", Wa_rintelproduct: "rintelproduct:processors/serverprocessors/intelxeonbronzeprocessorfamily,rintelproduct:processors/serverprocessors/intelxeonsilverprocessorfamily,rintelproduct:processors/serverprocessors/intelxeonplatinumprocessorfamily", It can be employed directly by the end-user or less skilled programmer to develop computer applications more rapidly than the conventional programming language.Wa_emtcontenttype: "emtcontenttype:datasheetsspecificationsandschematics/productspecification/datasheet",

It is also a non-structural programming language. Conversion time is slower than assembly level language.įourth-generation language (4GL) – 1985’s to till nowįourth-generation language (4GL) is more non-procedural, object-oriented, and conversational than prior language.The translator is necessary to translate languages.It is machine independent (portability).A used translator is a compiler or interpreter. Some advantages and disadvantages of this language as follows: And, also a structural oriented language and functional language. It is a third-generation programming language or procedural language. The translator is necessary to translate the program into machine code.

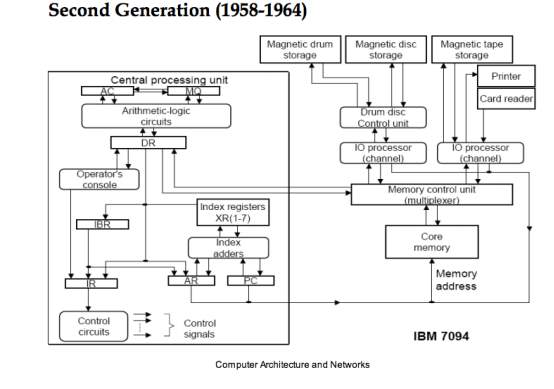
Similarly, it is easy to translate the language into machine language. Also, easy to modify errors and mistakes. This language is easy to program and understand. RAM and ROM concept was introduced in 2nd generation leaving behind magnetic drum concept. Speed of copmuter increased 10times first generation. Also size of computer in second generation was much smaller than one in first generation. Below given is a list of BSc Computer Science Subjects that might help the student in their curriculum. Some advantages and disadvantages of this language as follows: Second generation replaced vacuum tubes with transistors. BSc Computer Science syllabus contains core modules and are fundamental for the better understanding of the subject. Where it is a computer understandable language. It is very difficult to understand by us or humans. This language is written using binary codes (1’s and 0’s) and unique to each computer. Similarly, it is also a low-level language. The first-generation of language is machine level language. Fourth-generation language (1985’s to till now). High-level language or Third-generation language (1958’s to 1985’s). Assembly level language or Second-generation language (1950’s to 1958’s). Machine level language or First-generation language (the mid – 1940’s). The major types and generations of programming language are: 'These second-generation languages use abbreviations or mnemonics that are automatically converted to the appropriate sequence of 1s and 0s. This language comprises a set of instructions which are used to produce various kind of output. It is a computer language with its own syntax and semantics which applies to write programs. The language which is used to create programs is called a programming language. Later writers have somewhat redefined the meanings as distinctions previously seen as important became less. Historically, this classification was used to indicate increasing power of programming styles. Difference between third-generation language (3GL) and fourth-generation language (4GL) Programming languages have been classified into several programming language generations. Fourth-generation language (4GL) – 1985’s to till now. In the assembly language, symbolic names are used to represent the opcode and the operand part of the instruction. The second generation language comprises assembly languages that use the concept of mnemonics for the writing program. High-level language (3GL) – 1958’s to 1985’s The second generation programming language also belongs to the category of low-level- programming language. Assembly level language (1950’s to 1958’s). Machine level language (the mid-1940’s). The major types and generations of programming language are:.








 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
